Advanced Characterization Techniques
With different advanced characterization techniques, we examine the microstructure, nanostructure, and chemical properties of lead halide perovskites correlated to the electrical performance of the solar cell. For example, the following figure shows advanced characterization to study and understand the fundamental structure-properties:
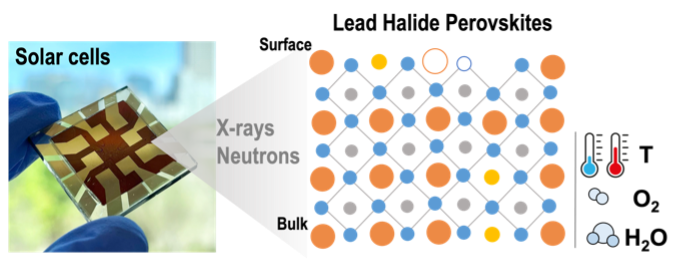
Through in-situ characterization methods, we study the effect of different external stimuli on degradation pathways to understand and optimize stability in perovskites for solar cells.
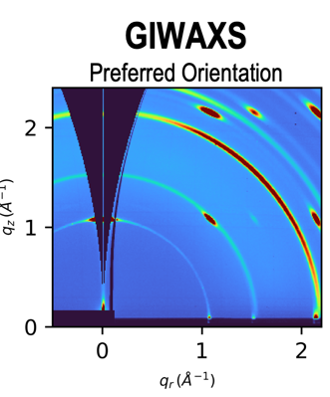
Synchrotron-based grazing incidence wide angle X-ray scattering (GIWAXS), with in-situ and high-throughput capabilities, is one of our core techniques to characterize the microstructure of polycrystalline thin films.
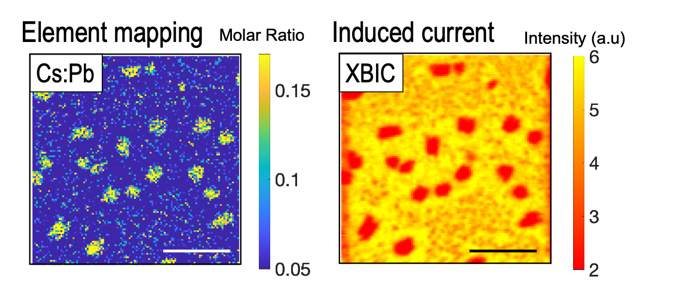
Synchrotron-based X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and X-ray beam induced current (XBIC) microscopy are used to correlate the elemental composition with the induced current in devices.
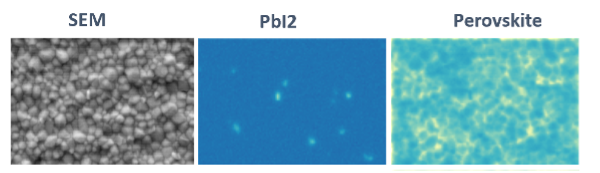
Cathodoluminescence SEM (CL-SEM) is used to correlate morphology and phase segregation of lead halide perovskites and thin films.
Details and References
We use synchrotron-based GIWAXS and XRF-XBIC characterization techniques as essential methods to characterize the lead halide perovskite thin films, and solar cells fabricated in our lab. In addition, we are exploring other advanced characterization techniques to learn more about the fundamental properties that control the material's properties such as CL-SEM, TEM, SAXS, GISAXS, and other neutron techniques.
- GIWAXS https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.2c02419
- GIWAXS https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202270350
- GIWAXS https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.2c02272
- GIWAXS/XRF https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c02036
- GIWAXS/XRF https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.1c03093
- GIWAXS https://doi.org/10.1039/D1EE02691G
- XRF https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b11637
- GIWAXS, XRF-XBIC https://doi.org/10.1021/acsenergylett.0c01964