Optoelectronic Devices
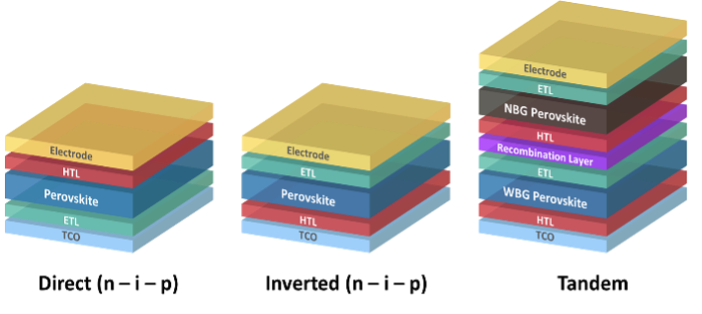
Fabrication of perovskite solar cells (PSCs) with architectures ranging from single junction (e.g., direct/inverted planar devices) to tandems with newly designed materials. We study interfaces between the perovskite film and the charge transport layers, which play a critical role in power conversion efficiency and stability.
Solar cell performance and stability is extensively researched under varying stress conditions such as light, temperature, humidity, gas, and electrical bias to provide a detailed understanding of the PSC operation via long-term reliability characterization (Litos Lite, Litos, and Paios platforms from Fluxim).
We fabricate and characterize organic and perovskite photodiodes based on bulk or planar heterojunctions with different organic and perovskite materials. We design photodiodes to achieve specific performances such as low noise, spectral sensitives from visible to near-infrared range, and fast response.
Details and References
Group Members: Sakshi, Sanggyun, Jingwei, Kunal, Carlo
Perovskite Solar Cell
Hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are one of the most promising technologies for solar energy harvesting. They are produced using low-cost materials and fabrication techniques such as low-temperature solution and vapor-based processing. PSCs have achieved power conversion efficiencies (PCEs) above 25%, which are competitive with traditional inorganic solar cells. The high efficiency of PSCs is due to their excellent light absorption, low recombination rates, and long carrier lifetimes. Perovskite materials offer high structural and compositional tunability, allowing optimization of their optical and electronic properties to improve the efficiency and stability of PSCs. Our research focuses on the development of deposition routes for perovskite semiconductors, study thin film crystallization and construct efficient solar cells with a focus on material composition and interfaces. Despite these advantages, long-term stability remains to be one of critical challenges toward PSC commercialization. In EML, we explore strategies to enhancing the stability of PSCs, including composition engineering of perovskite (e.g., methylammonium-free lead halide perovskites [1], interface engineering (e.g., PEAI & OABr passivation [2]), and charge transport modification (e.g., vapor phase infiltration [3]).
- Energy & Environmental Science 14, 6638-6654 (2021).
- Advanced Materials 34, 2204726 (2022). Rising Stars
- ACS Energy Letters 8, 844-852 (2023).
Perovskite Photodetector
By virtue of inherent material properties, hybrid organic-inorganic perovskite photodiodes are also good candidates for a variety of applications including wearable electronics, image sensors and machine vision with the promise for roll-to-roll, large-area and high throughput manufacturing. The performance of current state-of-art perovskite photodiodes is competitive to that of commercial silicon photodiodes in all metrics except for long-term stability. Our research focuses on the development of perovskite photodiodes with specific performances based on the design of perovskite semiconductors, optimization of device structure and integration of photodiodes with different optical structures such as filters.